Introduction
M y c o p l a s m a 세균은 세포벽이 없는 특징을 가지고 있는 Molicutes강에 속하는 세균으로 8개 속의 180여 종이 보고 되고 있으며, 세균 여과 필터를 통과할 수 있어 실험실 세포 오염에도 큰 문제를 야기한다[1]. 세포 배양 시 Mycoplasma 세균 오염의 원인은 초기 배양에 사용되는 조직, 혈청 또는 연구자에 의해서 유발되고, 세포주의 교차오염으로 인 해 다 른 세포주로 오염이 확산될 수 있다[2]. Mycoplasma 속 세균은 사람 및 동물의 호흡기, 생식기 등 각종 장기에 상주하며 다양한 질병을 일으키는 병원체로서 질병을 유발하는 것으로 알려져 있다[2]. 동물질병 관리 측면에서 Mycoplasma 속 세균 감염 여부를 신속히 진단하는 것은 경제적 측면이나 질병 관리측면에서 매우 중요하다[3]. Mycoplasma 감염 진단 방법들에는 다양한 방법이 개발되어 이용되고 있으나, 직접배양법은 시간이 많이 소요되고 배지 조성, 시료 특성 및 배양조건 등 많은 요소에 의해 영향을 받을 수 있다는 제한점이 있다[3,4]. Mycoplasma 신속 진단 방법으로 특이 병원체 염기서열 부위를 검출하는 polymerase chain reaction (PCR) 방법이 이용되고 있다[4,5]. 기존 연구자들이 보고한 Mycoplasma 세균을 검출하기 위한 PCR 방법들은 대 부 분 한 종 을 검 출 하 는 데 그 치 고 있 어 여 러 종의 Mycoplasma 세균들이 감염될 확률이 있는 경우에 다른 primer 쌍을 이용하여 여러 번의 PCR 분석을 수행해야 하는 불편이 있다[6]. 따라서 다양한 species를 가지고 있는 Mycoplasma 속 세균의 경우에 감염이나 오염 여부를 신속하게 한번의 작업으로 진단할 수 있는 기술의 개발이 요구되고 있다[6].
고양이에서 Mycoplasma 세균 감염에 의한 폐렴 또는 결막염을 유발하고 말에서 하부 호흡기 질환 또는 흉막염 [ 1 0 ] 을 유발할 수 있 는 것으로 보 고 되 고 있 다 [7 - 10]. 또한 살쾡이에서는 Mycoplasma 세균 감염에 의한 심한 호흡기 감염이 유발되고, 면역이 떨어진 고양이와 사람에서는 Mycoplasma 감염에 의한 관절염이 보고되고 있다[11,12].
본 연구는 고양이의 호흡기 병원체인 M y c o p l a s m a 세균을 검출할 수 있고, 신속하게 Mycoplasma species를 동시에 감별 진단할 수 있는 multiplex PCR을 개발하고자 계획되었다.
Meterials and Methods
본 연구에 사용된 균주는 American Type Cell Culture (ATCC)로부터 M. felis (ATCC 23391), M. canis (ATCC 19525), Helicobacter (H.) pylori (ATCC 43504)를 구입하여 사용하였다. H. pylori는 10% 우혈청이 첨가된 브루셀라 한천배지에 접종 후, 10% CO2 및 100% 습도가 유지되는 37℃ incubator에서 3일간 배양 하여 사용하였다. M. felis와 M. canis는 Hong et al [13]의 방법에 따라 준비된 배양 배지를 이용하여 37℃에서 5% CO2 함유 인큐베이터에서 14일 동안 배양하여 사용하였다.
배양한 M. felis와 M. canis 및 H. pylori 균주들의 DNA 추출은 bead beater-phenol 추출법을 사용하였다. 배양 균주들을 13,000 g에서 30분 동안 원심분리하여 얻은 펠렛 검체를 1 ㎖ 멸균 증류수가 들어있는 Mini-Bead Beater (Biospec product) 전용 2 ㎖ 튜브에 무균 채취하였다. 이후 멸균 3차 증류수에 부유시킨 glass bead (0.1 mm size, Biospec product) 200 ㎕와 phenol-chlorformisoamyl alcohol 용액 [50:49:1(v/v/v)] 200 ㎕를 넣어 Mini-Bead Beater (Biospec product)로 30초간 5,000 rpm으로 진탕하였다. 진탕 후 4 ℃에서 12,000 rpm으로 15분간 원심분리한 후 상층액을 멸균 2 ㎖ 튜브에 옮겼다. 3 M 초산나트륨 (sodium acetate) 10 ㎕와 ice-cold 에탄올 250 ㎕를 넣어 -20℃에서 10분간 정체시킨 후, 15,000 rpm으로 15분간 원심분리 하였다. 침전물은 70% 알코올로 세척하여 실온에서 건조시키고 Tris EDTA (pH 8.0) 60 ㎕에 용해시켜 실험에 사용하였다.
Mycoplasma 세균의 게놈 서열 중에서 Mycoplasma 세균 species에 특이적인 primer 세트를 제조하였다 (Table 1). PCR 반응은 DNA thermal cycler (PTC- 100 Thermocycler, MJ Research, USA)를 이용하여 반응을 실시하였다. PCR을 위한 반응 시약의 조성은 1㎕ forward 및 reverse primer (10pmol/㎕), 2.5 ㎕ 10×reaction buffer, 500 ㎛ deoxy nucleotide, 1.5U Taq polymerase를 각각 넣고, 총 반응량이 25 ㎕이 되도록 멸균된 증류수를 첨가하여 Table 1과 같은 조건으로 multiplex PCR 반응을 실시하였다.
M. felis (ATCC 23391), M. canis (ATCC 19525) 배양 균주와 대조균주로 H. pylori (ATCC 43504) 배양 균주를 사용하여 DNA 추출 후, 개발한 primer 쌍들로 구성된 multiplex PCR의 특이도 (specificity)를 확인하기 위해 Table 1과 같은 반응조건으로 PCR을 실시하여 특이도를 확인하였다. 특이도 검사는 3회 반복 시험을 실시하여 결과를 확인하였다.
개발한 primer의 민감도 (sensitivity)를 확인하기 위해 M. felis (ATCC 23391), M. canis (ATCC 19525)를 37℃에서 5% CO2가 함유된 인큐베이터에서 배양하였다. M y c o p l a s m a 배 양 균 주 들 의 D N A 를 추 출 하 여 S p e c t r o p h o t o m e t e r 로 DNA를 정량을 한 후 , 단계 희석하여 순수 분리된 M. felis DNA와 M. canis DNA을 104, 103, 102, 10 및 1 pg의 농도로 각각의 DNA를 정량하여 개발한 primer 쌍들로 구성된 multiplex PCR을 Table 1과 같은 반응조건으로 실시하여 민감도를 확인하였다. 민감도 검사는 3회 반복시험을 실시하여 결과를 확인하였다.
1년령의 Persian 암컷 고양이가 1주 전부터 콧물과 재채기의 호흡기 증상을 보여 비강에 멸균 면봉으로 비강 swab 채취를 실시하였다. 각 비강 채취 면봉들은 0.1 M PBS buffer 2 ㎖이 든 튜브에 넣고 vortex를 한 후 면봉을 제거하고, DNA 추출을 멸균 3차 증류수에 부유시킨 glass bead (0.1 mm size, Biospec product) 200 ㎕와 phenolchlorform- isoamyl alcohol 용액 [50:49:1 (v/v/v)] 200 ㎕를 넣어 Mini-Bead Beater (Biospec product)로 30초간 5,000 rpm으로 진탕하였다. 진탕 후 4℃에서 12,000 rpm으로 15분간 원심분리한 후 상층액을 멸균 2 ㎖ 튜브에 옮겼다. 3 M 초산나트륨 (sodium acetate) 10 ㎕와 냉각된 에탄올 250 ㎕를 넣어 -20℃에서 10분간 정체시킨 후, 15,000 rpm으로 15분간 원심분리 하였다. 침전물은 70% 알코올로 세척하여 실온에서 건조시키고 T r i s E D T A ( p H 8 . 0 ) 6 0 ㎕ 에 용 해 시 켜 실험에 사용하였다. 검사의 재현성 확인을 위해 3회 반복 시험을 실시하여 PCR 결과의 재현성을 확인하였다.
Results
본 연구에 사용된 Mycoplasma는 제작한 최적화 배지를 이용하여 37℃에서 5% CO2 함유 인큐베이터에서 14일 동안 배양하고, 배지의 색깔이 붉은색에서 노란색으로 변하면 Mycoplasma가 자란 것으로 추정하고, 색깔이 변한 최대희석 배수의 역지수를 색깔변화단위 (Color Change Unit)로 관찰하였다.
개발한 M y c o p l a s m a 의 다 중 검 출 p r i m e r 세트로 구성된 multiplex PCR의 반응을 확인하기 위해 M. felis와 M. canis에 특이적인 primers를 95℃에서 1분간 predenaturation을 실시 한 후 Table 1과 같은 조건으로 실시하여 나온 PCR 증폭 산물은 1.5% agarose에 넣고 100 volt에서 20분간 전기영동하여 ethidium bromide로 염색한 후 G e l - D o c u m e n t a t i o n s y s t e m ( U v i t e c cambridge, EEC)을 이용하여 Mycoplasma 세균에 특이적인 반응여부를 해당 밴드의 유무로 확인하였다. M. canis 특이 primer를 이용하여 template DNA를 증폭 하였을 때 247bp에서 특이적인 밴드를 확인하였고, M. felis 특이 primer를 이용하여 template DNA를 증폭한 결과 238 bp에서 특이적인 밴드를 확인하였다 (Fig. 1).
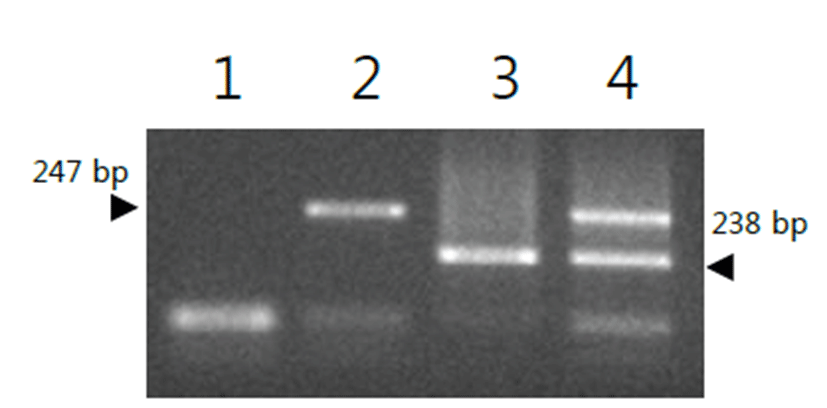
개발한 multiplex PCR의 특이도를 확인한 결과, M. felis와 M. canis DNA 샘플에만 특이적으로 반응하였고 대조균주인 H. pylori DNA 샘플에서는 반응하지 않았음을 확인 하였다 (Table 2).
| No. | Species | PCR results |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Helicobacter pylori | - |
| 2 | Mycoplasma canis | ++ |
| 3 | Mycoplasma felis | ++ |
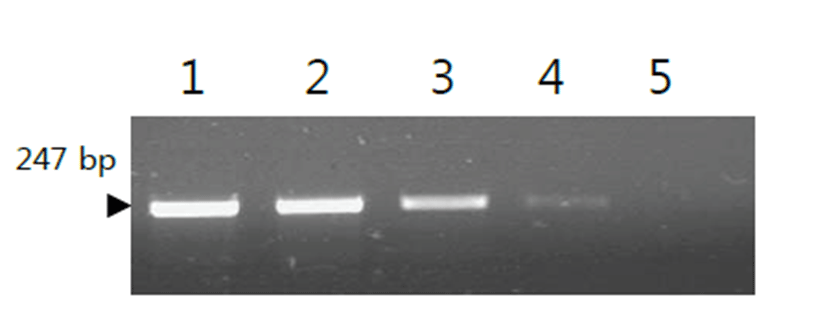
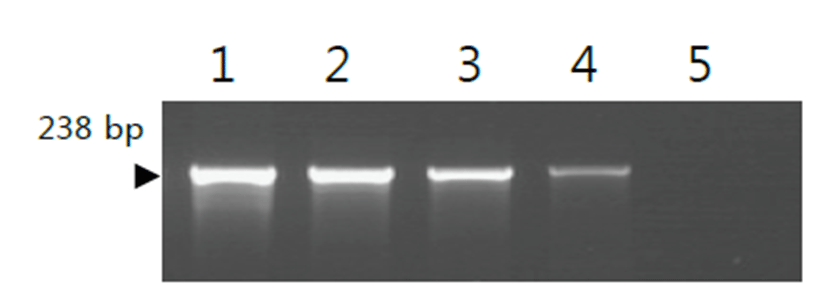
개발한 multiplex PCR의 민감도를 확인한 결과, M. canis DNA의 농도 1 pg은 검출하지 못하였으나, 10 pg 이상을 검출하여 102, 103, 104 pg으로 높을수록 민감도가 높아짐을 확인할 수 있었다(Fig. 2). 또한, M. felis DNA의 농도 1 pg은 검출하지 못하였으나, 10 pg 이상을 검출하여 102, 103, 104 pg으로 높을수록 민감도가 높아짐을 확인할 수 있었다 (Fig. 3).
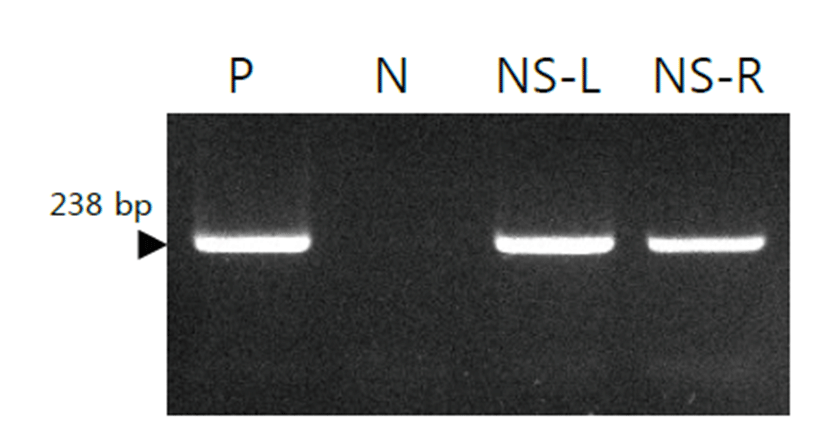
호흡기 증상을 가진 1년령의 Persian 암컷 고양이로부터 비강 안의 면봉 swab을 통하여 얻은 검체의 DNA로 개발한 primer 세트를 이용하여 multiplex PCR 검사를 실시한 결과, M. felis에 특이적인 238 bp의 밴드를 확인하였다 (Fig. 4).
Conclusion
Mycoplasma 세균은 사람과 동물의 호흡기나 생식기 등의 각종 장기에 심각한 질병을 초래하며, 특히 돼지와 소, 닭과 같은 동물에서는 폐렴과 같은 질병으로 폐사와 막대한 경제적 손실을 유발하는 병원체이다[14]. Mycoplasma 세균은 항생제에 내성이 있고 크기가 작아 여과에 의하여 문제가 해결되지 않으며, 모양이 불규칙한 다형성으로 관찰이 어렵다[1]. 또한, 세포배양에 오염된 Mycoplasma 세균과 동물에 감염된 Mycoplasma 세균을 진단하기 위한 많은 진단 키트가 개발되어 실용화 되고 있다[5,15]. 본 연구에서는 M. canis 및 M. felis를 동시에 진단할 수 있는 multiplex PCR을 개발하고 특이적으로 반응하는지를 확인하였다. PCR 진단은 병원체를 민감하게 검출할 수 있는 방법으로 유용한 검사법이지만 병원체 종류별로 각각의 검사가 이루어져야 한다[2]. 일반적으로 세포배양에 오염된 M y c o p l a s m a 검출 PCR기법의 민감도는 104 c f u / ㎖ 의 검출한계를 보인다고 알려져 왔 으 나 [ 4 , 6 ] , 최근에는 DNA 추출방법, nested PCR법, hot-start Taq DNA polymerase 사용으로 검출한계가 1-100 cfu/ml과 유사한 민감도를 보인다고 보고하고 있다[4,16,17]. 또한 template DNA의 pg 단위로 보고된 Mycoplasma PCR 검출 한계 들은 102 pg 이상인 것을 확인할 수 있었다 [13]. 본 연구에서는 M. canis 및 M. felis의 민감도는 DNA의 농도 10 pg 이상으로, 기존의 Mycoplasma 검출 연구결과들과 비교해 볼 때 유사 또는 보다 높은 민감도를 확인하였다. 특이도 또한 M. canis 및 M. felis 각각의 균주에 반응하는 것을 확인할 수 있었다. 대조균주로 마이코플라즈마와 거리가 있는 다른 종의 세균인 H. pylori와의 비특이 반응 여부를 검사한 결과 개발된 multiplex PCR 방법은 비특이 반응이 일어나지 않는 것을 확인할 수 있었다.
M. felis 확인을 하기 위한 방법으로는 특이 항체를 이용한 진 단 법 [ 1 8 ] , 형광항체반응[19], 면역반응검사[20], 간 접 혈 구 응 집 반 응 [ 2 1 ] 등 이 수 행 되 고 있 다 . 또 한 분자생물학의 발달로 M y c o p l a s m a 세균 s p e c i e s 에 특이적인 16S rRNA와 16S/23S rRNA intergenic spacer (IGS) DNA 부위를 활용한 진단이 개발되고 있다[4,22]. Brown et al [23]은 집고양이와 길고양이로부터 PCR 진단법으로 M. felis 진단에 대한 보고를 한 바 있다.
본 연구 결과, 고양이에서 문제가 될 수 있는 호흡기 Mycoplasma 세균 species 2종을 동시에 검출할 수 있는 multiplex PCR 기법이 개발되어 진단에 소요되는 시간을 경감하고 민감도와 특이도 또한 기존 방법 보다 우수한 것을 확인하였다. 연구의 제한점으로 임상 검체 적용 시험의 수가 적어 향후 보다 많은 임상 검체에 대한 확인 시험이 이루어질 계획이다.
본 연구를 통하여 개발된 multiplex PCR은 고양이의 Mycoplasma 세균 감염의 원인체 M. felis와 M. canis를 한 번의 검사를 통하여 동시에 감별 진단하는 데 이용될 수 있다.